Overview
CT Scan in India
A CT scan - also called computerized tomography or just CT - is an X-ray technique that produces images of your body that visualize internal structures in cross section rather than the overlapping images typically produced by conventional X-ray exams.
Conventional X-ray exams use a stationary X-ray machine to focus beams of radiation on a particular area of your body to produce two-dimensional images on film or a digital detector, much like a photograph. But CT scans use an X-ray unit that rotates around your body and a powerful computer. The result with CT scans is a set of cross-sectional images, like slices, of the inside of your body.
Doctors recommend a CT scan for a wide variety of reasons.
A conventional X-ray of your abdomen, for example, shows your bones as well as subtle overlapping outlines of your liver, stomach, intestines, kidney and spleen. A CT scan, however, clearly reveals these bones and organs as well as their inner structure and detailed anatomy of your pancreas, adrenal glands, kidneys and blood vessels.
Why is CT Scan Done ?
Your doctor may recommend a CT scan to help : -
- Diagnose muscle and bone disorders, such as bone tumors and fractures.
- Pinpoint the location of a tumor, infection or blood clot.
- Guide procedures such as surgery, biopsy and radiation therapy.
- Detect and monitor diseases such as cancer or heart disease.
- Detect internal injuries and internal bleeding.
CT scans can be done even if you have a pacemaker or an internal cardioverter defibrillator (devices implanted in your chest to help regulate your heartbeat). However, if you're pregnant or suspect you might be, tell your doctor. Your doctor may suggest postponing the procedure or choosing an alternative exam that doesn't involve radiation, such as an ultrasound or MRI.
Risks of CT Scan
CT scan risks are similar to those of conventional X-rays. During the CT scan, you're briefly exposed to radiation. But doctors and other scientists believe that CT scans provide enough valuable information to outweigh the associated risks.
Be sure to inform your doctor if : -
You're pregnant. If you're pregnant, your doctor may recommend another type of exam to reduce the possible risk of exposing your fetus to radiation.
You have asthma or allergies. If you have had a prior reaction to contrast media or have asthma or allergies, there's an increased risk of a reaction to the contrast medium.
You have certain medical conditions. Diabetes, asthma, heart disease, kidney problems or certain thyroid conditions may increase your risk of a reaction to contrast media.
How you prepare for CT Scan ?
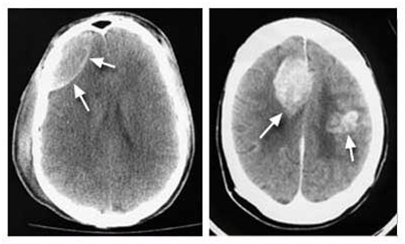
[ CT scan images of the brain ]
Left : - Arrows indicate an epidural hematoma, a collection of blood between the skull and the outer covering of the brain, that's compressing the frontal lobe.
Right : - Contrast medium injected into a vein during this CT scan of the head highlights tumors in both sides of the brain.
How you prepare for a CT scan depends on which part of your body is being scanned. You may be asked to remove your clothing and wear a hospital gown. You'll need to remove any metal objects, such as jewelry, that might interfere with image results.
Preparation sometimes involves fasting
Some CT scans require you to drink a contrast liquid before the scan or have contrast injected into a vein in your arm during the scan. A contrast medium blocks X-rays and appears white on images, which can help emphasize blood vessels, bowel or other structures. If your test involves a contrast medium, your doctor may ask you to fast for a few hours before the test.
Depending on the part of your body being scanned, your doctor may ask you to take laxatives, enemas or suppositories, or temporarily modify your diet.
Reactions to contrast medium
Although rare, the contrast medium involved in a CT scan poses a slight risk of allergic reaction. Most reactions are mild and result in hives or itchiness. For people with asthma who become allergic to the contrast medium, the reaction can be an asthma attack.
In rare instances, an allergic reaction can be serious and potentially life-threatening - including swelling in your throat or other areas of your body. If you experience hives, itchiness or swelling in your throat during or after your CT exam, immediately tell your technologist or doctor.
If you've had a reaction to a contrast medium in the past, and you need a diagnostic test that may require a contrast medium again, talk to your doctor. Be sure to let your doctor know if you have kidney problems, since contrast material that's injected into a vein is removed from your body by your kidneys and could potentially cause further damage to your kidneys.
Preparing your small child for a scan
If your infant or toddler is having the CT scan, the doctor may give your child a sedative to keep him or her calm and still. Movement blurs the images and may lead to incorrect results. Ask your doctor how best to prepare your child.
What you can expect of CT Scan ?
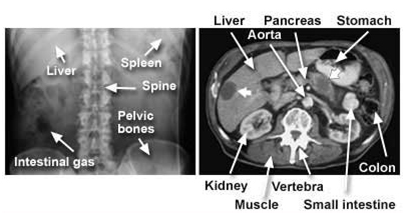
[ CT scan image of the abdomen ]
[ CT scan slices ]
CT scans allow doctors to see multidimensional images (slices) of your body. This slice shows heart and lung tissue.
Left : -Conventional X-ray film shows bones and vague outlines of organs.
Right : -CT with contrast medium clearly shows several organs and blood vessels. Short, thick arrows show a tumor in the pancreas that has spread (metastasized) to the liver.
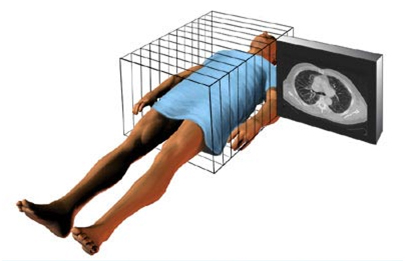
During a CT scan, you lie on a table inside a doughnut-shaped machine called a gantry. An X-ray tube inside the machine rotates around your body and sends small doses of radiation through it at various angles. As X-rays pass through your body, different tissues absorb different amounts of radiation.
Detectors inside the gantry measure the radiation that passed through your body and converts it into electrical signals. A computer gathers these signals and assigns them a color ranging from black to white, depending on signal intensity. The computer then assembles the images and displays them on a computer monitor.
You can have a CT scan in a hospital or an outpatient facility. Expect the exam to last no longer than an hour, depending on the preparation needed and whether it includes the use of a contrast medium. The scan itself may take less than a minute on the newest machines. Most scans take just a few minutes to complete.
During the CT scan, you lie on a narrow table that slides through the opening of the gantry. You may lie on your back, side or stomach, depending on the area to be scanned. The table can be raised or lowered. Straps and pillows may help you stay in position. During a CT scan of the head, the table may be fitted with a special cradle that holds your head still.
What the device does ?
As the X-ray tube rotates around your body, the table slowly moves through the gantry. While the table is moving you may need to hold your breath to avoid blurring the images. You may hear clicking and whirring noises. Each rotation yields several images of thin slices of your body.
During this time, a technologist in a shielded room supervises the CT scan and monitors the images as they appear on the computer screen. The technologist can see and hear you, and you can communicate via intercom.
CT scans are painless. If your exam involves use of an intravenous contrast medium, you may feel a brief sensation of heat or experience a metallic taste in your mouth. If you receive the contrast medium through an enema - to help highlight your lower gastrointestinal region - you may feel a sense of fullness or cramping.
After the exam you can return to your normal routine. If you were given a contrast medium, your doctor, a nurse or the CT technologist performing the scan may give you special instructions. You may be asked to wait for a short time in the radiology department to ensure that you feel well after the exam. After the scan, you'll likely be told to drink lots of fluids to help your kidneys remove the medium from your body.
During your small child's exam
If an infant or small child is having the CT scan, you may be allowed to stay with your child during the test. If so, you may be asked to wear a lead apron to shield you from X-ray exposure.
Results of CT Scan
CT images are stored as electronic data files and usually reviewed on a computer. A radiologist interprets these images and sends a report to your doctor.
The list of of Health Check up and screening Hospitals in India is as follows : -
 |
Apollo Hospitals, Bangalore, India |
 |
Apollo Hospital, Chennai, India |
 |
Apollo Hospitals, Hyderabad, India |
 |
Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Delhi, India |
 |
Apollo Gleneagles Hospital, Kolkata, India |
 |
Apollo Hospital, Goa, India |
 |
Wockhardt Hospital, Bangalore India |
 |
Wockhardt Hospital, hyderabad, India |
 |
Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India |
 |
Wockhardt Hospital and Kidney Institute, Kolkata, India |
 |
Fortis Hospital, Delhi, India |
 |
Fortis Hospital, Mohali, India |
 |
Fortis Hospital, Noida, India |
 |
Escorts Heart Institute Hospital, Delhi, India |
 |
Manipal Hospital, Bangalore, India |
 |
MIOT Hospital, Chennai, India |
 |
Narayana Hrudayalaya Heart Hospital, Bangalore, India |
 |
Sparsh Hospital, Bangalore, India |
 |
Narayana Cancer Hospital, Bangalore, India |
 |
Artemis Hospital, Gurgaon ( Delhi ) , India |
 |
Max Super Specialty hospital, Delhi, India |
 |
Max Devki Devi Heart and Vascular hospital, Delhi, India |
 |
Max Health Check Centre, Delhi, India |
 |
BGS Global Hospital, Bangalore, India |
 |
BGS Global Hospital, Chennai, India |
 |
BGS Global Hospital, Hyderabad, India |
|
For more information, medical assessment and medical quote
send your detailed medical history and medical reports
as email attachment to
Email : - info@wecareindia.com
Call: +91 9029304141 (10 am. To 8 pm. IST)
(Only for international patients seeking treatment in India)
| |
|
|
