Genetic Infertility Treatments in India
What is DNA ?
DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) is a code inside cells to tell the body what it needs to function and what to look like. The code is made up of 4 different chemical units called bases. The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The code, if you were to read it, would look something like this:
..CGTAGCTTACTTTAGGCTAGCAAACGCATC....
A gene is a small section of the code (though much longer than this example) that can be decoded by the cell to mean something. A single gene might be responsible for any aspect of your body's function or appearance, like making a certain protein, or the colour of your eyes. If there is an error in the code for a gene the product will be faulty (see genetic mistakes). When a cell divides, identical copies of the DNA must be made and distributed evenly into the new cells e.g. when a baby is developing or when we make new blood or skin cells.
WE ARE HAPPY TO HELP YOU 24/7 Regarding Genetic Treatment India
We are here for giving you full information and support as well, if you have any doubt and want to ask some question from our expert's for Genetic Medicine Treatment India, so email us on: info@wecareindia.com and call: +91 9029304141 (10 am. To 8 pm. IST)
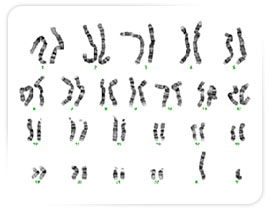
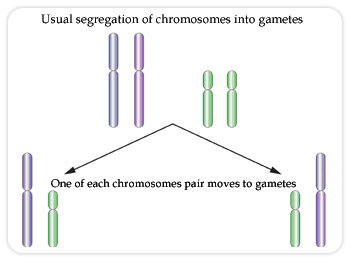
What are Chromosomes?
Packaging the DNA into chromosomes ensures that the genetic material is copied and distributed evenly when a cell divides. Chromosomes can only be seen under the microscope when a cell is dividing.
Long strings of DNA, containing hundreds of genes each, coil up in the form of chromosomes. In normal human cells there are 46 chromosomes There is one pair of sex chromosomes (two X chromosomes for females and one X and one Y chromosome for males) and 22 pairs of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) numbered 1-22. When a cell divides the DNA is copied and 1 copy of each chromosome is distributed into each new cell (mitosis). The new cells are an identical copy of the previous cell. When producing sperm and eggs, the cells divide so that there are only 23 chromosomes - one of each pair (meiosis).
Genetic Mistakes - Genetic Treatment India
Sometimes mistakes can happen in the copying of the code when a cell divides.
A section of the DNA can be missed out
GTCAACTGATCGATCGGATCGA
GTCAAC___TCGATCGGATCGA
The wrong base might be copied
GTCAACTGATCGATCGGATCGA
GTCAACTGCTCGATCGGATCGA
Once these errors are made, the gene may be faulty and not function properly. It may cause a genetic disease, such as cystic fibrosis. The faulty gene will be copied exactly and can be passed down from generation to generation.
Chromosome errors
 When a cell is dividing, sometimes a whole chromosome can end up in the wrong cell, so that the cell has the wrong number of chromosomes (aneuploidy). One cell will have one too many chromosomes (chromosome gain) and one will have one too few (chromosome loss). If there is an extra chromosome, the cells have extra DNA and if there is one missing there will be less. This is rather like having either too many or not enough ingredients for a recipe. These mistakes can happen when any cell is dividing but if they occur during the formation of sperm and eggs cells, it will affect the genetic makeup of the embryo .
When a cell is dividing, sometimes a whole chromosome can end up in the wrong cell, so that the cell has the wrong number of chromosomes (aneuploidy). One cell will have one too many chromosomes (chromosome gain) and one will have one too few (chromosome loss). If there is an extra chromosome, the cells have extra DNA and if there is one missing there will be less. This is rather like having either too many or not enough ingredients for a recipe. These mistakes can happen when any cell is dividing but if they occur during the formation of sperm and eggs cells, it will affect the genetic makeup of the embryo .
How do we test DNA
 Pieces of chromosomes can sometimes be rearranged, so that one piece of a chromosome is stuck on another (translocation) A handy way to think about this is if you imagine that you have two complete sets of Encyclopaedia Britannica in your house, stored in a very orderly fashion.
If, for some reason, the order of the two sets of books is rearranged, it doesn't bother you, because you still have 2 copies of all the volumes.
But if you then swapped a set of the books with someone else, not realising that their order had been changed, you might find yourself with two copies of volume 6, but none of volume 11! This is very irritating if you need to know something in Volume 11. Imagine if the information in that book was crucial for your survival, as is almost always the case with chromosomes.
Pieces of chromosomes can sometimes be rearranged, so that one piece of a chromosome is stuck on another (translocation) A handy way to think about this is if you imagine that you have two complete sets of Encyclopaedia Britannica in your house, stored in a very orderly fashion.
If, for some reason, the order of the two sets of books is rearranged, it doesn't bother you, because you still have 2 copies of all the volumes.
But if you then swapped a set of the books with someone else, not realising that their order had been changed, you might find yourself with two copies of volume 6, but none of volume 11! This is very irritating if you need to know something in Volume 11. Imagine if the information in that book was crucial for your survival, as is almost always the case with chromosomes.
We Care Health Services Hospitals
Copyright © 2009 - 2015 We Care India. All Rights Reserved.
Home | About Us | Site Map | Get a Quote | Disclaimer | Advertise With Us | Contact Us