Liver Cancer Treatment India at affordable cost
What is liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC)?
Best Hospital in India for Liver Cancer : Liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) is a cancer arising from the liver. It is also known as primary liver cancer or hepatoma. The liver is made up of different cell types (for example, bile ducts, blood vessels, and fat-storing cells). However, liver cells (hepatocytes) make up 80% of the liver tissue. Thus, the majority of primary liver cancers (over 90 to 95%) arises from liver cells and is called hepatocellular cancer or carcinoma.
If you need best hospital for liver cancer treatment in India, so choose India hospital tour that helps you to find best liver cancer hospital in India. We will provides you best service with low cost liver cancer treatment India.
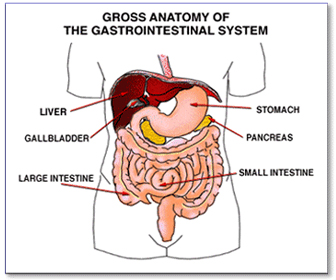 When patients or physicians speak of liver cancer, however, they are often referring to cancer that has spread to the liver, having originated in other organs (such as the colon, stomach, pancreas, breast, and lung). More specifically, this type of liver cancer is called metastatic liver disease (cancer) or secondary liver cancer. Thus, the term liver cancer actually can refer to either metastatic liver cancer or hepatocellular cancer. The subject of this article is hepatocellular carcinoma, which I will refer to as liver cancer.
When patients or physicians speak of liver cancer, however, they are often referring to cancer that has spread to the liver, having originated in other organs (such as the colon, stomach, pancreas, breast, and lung). More specifically, this type of liver cancer is called metastatic liver disease (cancer) or secondary liver cancer. Thus, the term liver cancer actually can refer to either metastatic liver cancer or hepatocellular cancer. The subject of this article is hepatocellular carcinoma, which I will refer to as liver cancer.
Functions of the liver
The liver is the largest organ inside the body. It is located on the right side of the abdomen and is protected by the ribcage. The liver will function normally with only a small portion of it in working order.
Its functions include : -
- Destroying harmful substances, such as alcohol, and getting rid of waste products
- Converting food containing fats and sugars to be used by the body for energy
- Producing bile to help the digestion of food.
Primary liver cancers
Primary liver cancer is one of the less common cancers in Victoria with about 260 people diagnosed each year. It is more common in men and people aged over 65 years. Most primary liver cancers start in liver cells (hepatocellular carcinoma); others start in a bile duct (cholangiocarcinoma).
In the Western world, most people who develop primary liver cancer also have cirrhosis of the liver. This is scarring of the liver due to causes including heavy alcohol drinking over a long period of time. However, only a small number of people who have cirrhosis of the liver develop primary liver cancer. Infection with hepatitis B, C or D can also increase the risk of cirrhosis and, later, primary liver cancer.
Causes and Risk factors
The exact cause of primary liver cancer is still unknown. There are a number of factors, however, that increase your risk of developing it.These include : -
- Liver cirrhosis In the Western world, most people who develop hepatoma usually also have a condition called cirrhosis of the liver. This is a fine scarring throughout the liver which is due to a variety of causes including infection and heavy alcohol drinking over a long period of time. However, only a small proportion of people who have cirrhosis of the liver develop primary liver cancer.
- Infection Infection with either the hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus can lead to liver cancer. This can also be the cause of cirrhosis, which in turn increases the risk of developing hepatoma. The risk is greater in those that also smoke.
- Inherited conditions People who have a condition called haemochromatosis, which causes excess deposits of iron in the body, or the condition alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency, have a higher chance of developing hepatoma.
- Aflatoxin In Africa and Asia a poison called aflatoxin, found in mouldy peanuts and grain, is a major cause of hepatoma.
Diagnosis
Liver cancer is usually diagnosed with a number of different tests, which may include : -
- Blood tests - to check your general health and to check for a chemical usually found in increased levels in people with primary liver cancer.
- Ultrasound - a picture of the liver is taken using sound waves.
- CT scan - a specialised x-ray taken from many different angles to build a three-dimensional (3-D) picture of the body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - similar to a CT scan, but uses magnetism instead of x-rays to build a picture of the body.
- Liver biopsy - a small piece of liver tissue is removed with a needle and examined for cancer cells.
- Laparoscopy - a small cut in the lower abdomen allows a thin mini-telescope (laparoscope) to be inserted to look at the liver and take a sample of the liver tissue
How is liver cancer treated ?
Transplant: For some patients a liver transplant may be an option, but only if the cancer has not spread to other organs and a suitable liver can be 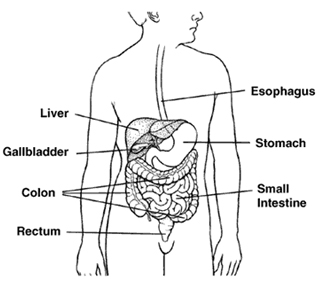 found.
found.
Surgery: In cases where the cancer has been found early and the liver is otherwise healthy, or has only early-stage cirrhosis, doctors will remove the portion of the liver where the tumor is located, a process called surgical resection.
Cryosurgery (also called cryotherapy): This is the use of extreme cold produced by liquid nitrogen (or argon gas) to destroy abnormal tissue.
Ablation: Some liver tumors can be destroyed by processes called ablation. Radio frequency ablation kills liver tumors by heating them to high temperatures with microwave probes. Another ablation technique destroys tumors by injecting them with ethanol, a form of alcohol.
Chemotherapy: Although chemotherapy cannot cure liver cancer, a new technique called transarterial chemoembolization may help prolong life for liver cancer patients. In this procedure, chemotherapy drugs are injected into the blood vessels that feed the tumors. This delivers a high dose of chemotherapy to the tumor while decreasing the flow of blood that feeds the tumor.
Radiation therapy: In some cases, doctors may try to reduce the size or slow the growth of liver cancer with radiation, or high-energy x-rays. Traditional radiation therapy also destroys healthy liver tissue, so doctors are experimenting with new techniques that deliver the radiation with higher precision.
The list of of Knee Joint Replacement Hospitals in India is as follows : -
- Apollo Hospitals, Bangalore, India
- Apollo Hospital, Chennai, India
- Apollo Hospitals, Hyderabad, India
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Delhi, India
- Apollo Gleneagles Hospital, Kolkata, India
- Apollo Hospital, Goa, India
- Wockhardt Hospital, Bangalore India
- Wockhardt Hospital, hyderabad, India
- Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India
- BGS Global Hospital, Chennai, India
- Fortis Hospital, Delhi, India
- Fortis Hospital, Mohali, India
- Fortis Hospital, Noida, India
- Manipal Hospital, Bangalore, India
- BGS Global Hospital, Hyderabad, India
- MIOT Hospital, Chennai, India
- Sparsh Hospital, Bangalore, India
- Artemis Hospital, Gurgaon ( Delhi ) , India
- Max Devki Devi Heart and Vascular hospital, Delhi, India
- BGS Global Hospital, Bangalore, India
For more information, medical assessment and medical quote send your detailed medical history and medical reports as email attachment to Email : - info@wecareindia.com Call: +91 9029304141 (10 am. To 8 pm. IST) (Only for international patients seeking treatment in India)
We Care Health Services Hospitals
Copyright © 2009 - 2015 We Care India. All Rights Reserved.
Home | About Us | Site Map | Get a Quote | Disclaimer | Advertise With Us | Contact Us